Fluid lines in industrial machinery and automotive systems are unsung heroes. These vital components move hydraulic oil, brake fluid, and coolant around your equipment but often don’t get noticed until a problem arises.
Learning how to safeguard these essential pathways can save you time, money, and headaches while ensuring maximum performance and life.
Fluid Line Protection
Fluid lines face many threats as they perform their daily duties. These essential components have to be shielded from UV radiation, extreme temperatures, and mechanical impacts like rock debris and accidental blows.
One single failure of your fluid lines can result in catastrophic consequences, ranging from system failure to environmental contamination and cost-creating downtime.
Common Fluid Line Integrity Threats
Fluid lines face various, persistent threats. Road debris causes immediate physical damage, while continuous vibration leads to gradual wear and tear.
Chemical exposure from road salt, oil, and other substances accelerates corrosion, and extreme temperatures impact the material properties of both lines and their protective coverings.
Key Protection Methods
The best way to protect your fluid lines is by installing a high-quality gravel guard. These tough shields will act as an initial barrier to flying debris, stones, and other objects that might otherwise cause considerable damage to your fluid lines.
Proper routing and securing of fluid lines play an important role in their long-term service. Lines should be mounted away from heat sources and moving parts.
Clamps and brackets used to secure lines must not permit excessive movement while still allowing for normal system flexing and thermal expansion.
Best Installation and Maintenance Practices
Professionals should install it to protect your fluid lines. This includes:
- Proper placement of protective sleeves and shields to maximize coverage while still allowing access for maintenance.
- Careful attention to routing paths that minimize exposure to heat sources and moving components.
- Regular inspection points should be easily accessible, allowing for routine maintenance checks without compromising protection.
- Spacing must be adequate for lines and other components to prevent rubbing and chafing, including the proper use of cushioned clamps and sufficient clearance around all bends and connection points.
- Abrasion-resistant sleeves have been installed at potential contact points for added protection.
Material Selection and Compatibility
Selecting the most suitable materials for both your fluid lines and protection parts is really the key to a long period of reliability for modern fluid lines, which, in various materials, could be used suitably for all the applications concerned, as well as specific operating conditions.
Similarly, protective parts must select suitably matching compatibility with either fluid lines protecting them or operational environments.
When selecting materials, consider factors such as:
- temperature resistance
- chemical compatibility
- flexibility requirements
- pressure ratings
High-performance synthetic rubbers and advanced polymers often provide the best combination of protection and durability for most applications.
Regular Inspection and Maintenance Protocols
The importance of having a thorough inspection and maintenance program cannot be overlooked when it comes to your vehicle’s fluid line protection systems.
Regular visual inspections should be done to look for signs of wear, damage, or degradation both in the lines themselves and in their protective components.
Key inspection points also include checking for evidence of chafing or rubbing, checking how securely the mounting points and clamps are fastened, and confirming the presence of fluid leakage or seepage.
The places where lines pass near moving parts or sources of heat must be inspected more carefully since they are the most prone areas to damage.
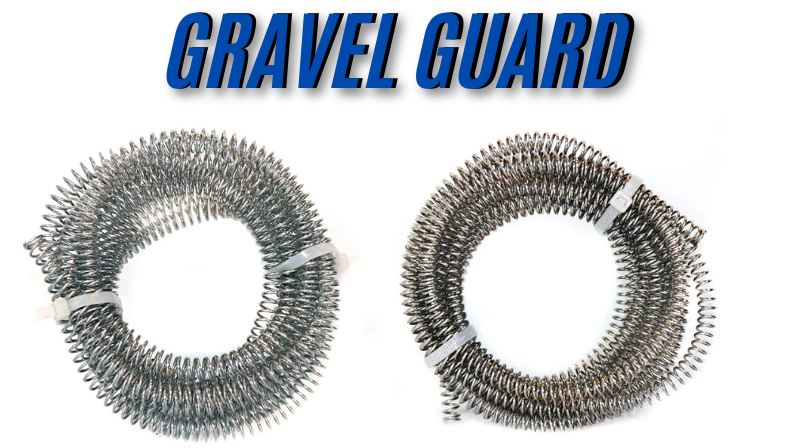

Advanced Protection Technologies
Modern technology has introduced many innovative solutions to protect the fluid line. Among them, advanced coating materials with physical and chemical protection, smart sensors that can predict failures, and composite materials offering superior protection with reduced weight and complexity are used.
Environmental Considerations
Different operating environments present unique challenges to fluid lines. Saltwater corrosion is a key threat in marine applications. UV radiation and extreme temperature fluctuations are the greatest threats in desert applications.
Knowing your particular operating environment is essential in developing effective protection measures.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
While comprehensive fluid line protection may seem prohibitively expensive on the front end, the end benefits far surpass the costs involved.
Consider a few of the potential expenses a system failure creates: emergency repair, lost time, environmental remediation, and potential liability risks. Proper protection is an investment in your systems’ reliability and longevity.
Looking to the Future
As technology advances, new methods and materials for fluid line protection are being developed.
Thanks to innovations like sophisticated monitoring systems and self-healing materials, fluid line protection appears to have a bright future. If you keep up with these advancements, you can make smarter decisions concerning system protection.
Final Thoughts
Protecting your fluid lines prevents failures and ensures the long-term reliability and efficiency of your entire system. The appropriate protection methods, choice of materials, and regular inspection protocols can extend the life of fluid lines significantly and avoid costly failures.
Remember that fluid line protection is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Your specific application, operating environment, and maintenance capabilities should all factor into your protection strategy.
Taking a comprehensive approach to fluid line protection will ensure optimal performance and reliability for years to come.